-
Module 2.0 How to be Successful in this Course
-
Module 2.1 Introduction to Natural Gas
-
Module 2.2 The Natural Gas Industry in British Columbia
- Overview
- Learning Outcomes
- Natural Gas Science – The Simple Version
- Natural Gas Science – Chemistry
- Natural Gas Science – Physics
- Natural Gas Science – Units of Measurement
- Natural Gas Science – Geology
- Natural Gas Resources and Uses
- Oversight of the Natural Gas Industry
- Understanding Land Rights and Natural Gas
- Energy and the Future
-
Module 2.3 Upstream – Well Site Selection, Preparation and Drilling, Completion, Production, Water Recycling, and Reclamation
- Learning Outcomes
- The Upstream Sector – Extraction and Processing
- The Upstream Sector – Exploration and Site Selection
- The Upstream Sector – Preparation and Drilling
- The Upstream Sector – Completion
- The Upstream Sector – Production
- The Upstream Sector – Water Recycling
- The Upstream Sector – Reclamation
- Upstream Companies and Jobs in British Columbia – Companies
- Upstream Companies and Jobs in British Columbia – Industry Associations
- Upstream Companies and Jobs in British Columbia – Professional Associations
- New Vocabulary
-
Module 2.4 Midstream – Transportation, Processing, Refining
- Learning Outcomes
- The Midstream Sector
- The Midstream Sector – Processing Natural Gas
- The Midstream Sector – Liquefied Natural Gas
- The Midstream Sector – An Emerging Industry
- The Midstream Sector – Processing LNG
- The Midstream Sector – Proposed LNG Projects in British Columbia
- Transportation
- Midstream Companies and Jobs in British Columbia
-
Module 2.5 Downstream – Refining and Markets
-
Module 2.6 Health and Wellness in the Natural Gas Industry
-
Module 2.7 Safety
-
Module 2.8 Terminology and Communication
-
Module 2.9 Jobs and Careers
- Learning Outcomes
- Industry Outlook
- Technology is Changing Workforce and Skills
- Employment in the Natural Gas Industry
- Employment in the Natural Gas Industry – Types of Employment
- Employment in the Natural Gas Industry – Range of Jobs
- Employment in the Natural Gas Industry – High Demand Jobs and Occupations
- Occupational Education and Training
-
Module 3.0 How to be a Valued Employee
-
Module 3.1 Identifying Interests and Skills
-
Module 3.2 Looking for Employment in Natural Gas
-
Module 3.3 Applying for Employment in Natural Gas
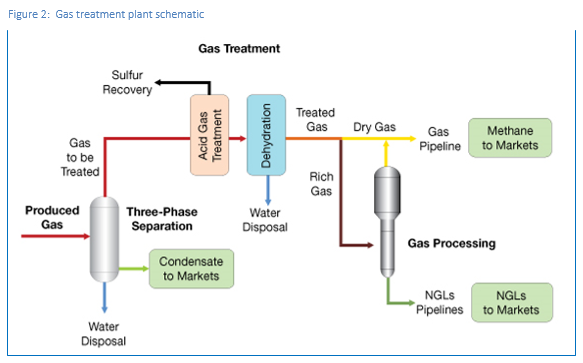
Production processes involve readying natural gas from the well for commercial use and transportation. Gas flows through gathering pipelines to processing plants called gas plants. Gas from the well is often mixed with water, impurities, and other gases such as sulphur dioxide and carbon dioxide, which need to be removed through a series of processes. The gas also needs to be condensed to the right pressure for transportation through pipelines. These production processes generally take place in a gas treatment plant, shown in Figure 2: Gas treatment plant schematic.
Gas Processing
I f the gas from the upstream sector contains sulphur compounds, it is termed “sour” or “sour gas”. Sour gas is extremely dangerous and requires special equipment and procedures in order to safely process and handle it. Gas processing plants handling large
f the gas from the upstream sector contains sulphur compounds, it is termed “sour” or “sour gas”. Sour gas is extremely dangerous and requires special equipment and procedures in order to safely process and handle it. Gas processing plants handling large
volumes of sour gas will include a sulphur recovery facility to produce elemental sulphur for sale to fertilizer manufacturers and other industries. The British Columbia gas industry as of 2019 included 25,434 wells, 50,047 km of pipelines (11,000 kilometers
of which is sour gas), 107 gas processing plants, and 6 liquefied natural gas facilities 2 These pipelines safely transport sour natural gas, crude oil, high vapor pressure substances (propane, butane), water and of course natural gas. Regular maintenance
and inspections are important to all pipelines and are particularly important for the sour gas segment of the industry because sulphur compounds are highly corrosive.
1Pipeline Performance in British Columbia 2018, BC Oil & Gas Commission, P 3
2The BC Oil and Gas Commission, 2019, Quick Facts, P 1
Video 5: Natural Gas Production and Marketing in the Marcellus Shale (9 minutes 43 seconds)

Learning Activity 4: Production
Instructions
Watch Video 5 and answer the following questions.
- Is natural gas ready for sale straight from the well? Why or why not?
- What preventative measures are in place to protect the environment in this phase of production?
- What does a “separator” do?
- What does a “sales meter” do?
- What is a “CDP?”
- What is a “dehydrator?” What does it do?
- What is “glycol?”
- What are pipelines used for?
- What are some preventative measures that are taken when installing a new pipeline?
- What is a “silt fence” and a “silt sock” and what are they used for?
- What is the purpose of the coating on the outside of the pipe used in the pipeline?
- How are the sections of pipe joined?
- Why is the pipeline x-rayed?
- How is the pipeline tested before gas is pumped through it?
- What steps are taken to check for leaks after the pipeline is installed?
